- Main Page
- Products
- Products
- PCR Products
- Nucleic Acid Purification
- DNA/RNA Electrophoresis
- Protein Electrophoresis
- Imaging
- Cell Biology
- Laboratory Instruments
- Laboratory Plastic
- Technology
- Company
- News
- Distributors
-
-
For all cell lines, even iPS
-
Fast
-
Serum-free
-
Stable
-
European patent
The freezing medium BambankerTM offered by the Japanese company Lymphotec was developed initially just for their own R&D projects. They needed a suitable medium for long-term storage of highly sensitive cell lines, such as lymphocytes.
Thanks to the innovative formulation of the new freezing medium, an European Patent (EP 1347040) was granted and the development of this media was made commercially available. Today this innovative cell freezing medium BambankerTM is the market leader in Japan and characterized by many different published articles with very sensitive cell lines all over the world.
Universal - even for preservation of stem cells
All common cell lines can be preserved resulting in a high number of intact cells after thawing. Recovery rates of even sensitive cells is much higher compared to regular media.
User friendly with a high stability
No dilution, no addition of components (like DMSO or glycerol). No programmable freezer and no sequential freezing steps are required - saves a lot of time. Shelf life is 24 months, when stored in a fridge (2 - 10 °C).

Innovative
Because of the unique formulation, Lymphotec Inc. has got a European patent (EP 1347040).

Flexible
We can offer 1 x 20, 5 x 20 and 1 x 120 ml bottles.

Some cell lines which already were successfull tested with Bambanker:
- P3U1 (mouse myeloma cell line)
- K562 (human leukemia cell line)
- Human gastric epithelial cell line
- Human γδT cell
- Daudi (human B cell line)
- PC12 (rat-derived adrenal pheochromocytoma)
- Human B cell line
- OKT4 (mouse hybridoma cell line)
- Monkey B cell line
- Mouse ES cell line
- Activated lymphocyte cell line derived from human peripheral blood
- Activated lymphocyte cell line derived from mouse spleen
- Astrocyte cell line dervied from brain tissue of newborn Wistar rats (Rattus norvegicus)
"JCRB cell bank has carried out cell bank business for 30 years and we currently store 1400 types of cell lines. In 2013, we offered about 4,300 ampules for a fee to domestic and foreign researchers. Due to the high number and the wide variety of cell lines, we had some problems.
Thus some users complained that their cell lines of dying after thawing, resulting in unsuccessful cultivation. Especially four types of cell lines were a problem which had to be urgently improved. Therefore, we compared Bambanker™ with our currently used commercial preservation medium in a cryopreservation test. The cell lines, which were stored with Bambanker™, showed much higher cell proliferation than cells, which were stored with our currently used commercially available product. Surprisingly, with Bambanker™ we got for all four cell lines very reproducible results.
In addition, Bambanker has no differences between the lots since it does not contain serum. We are very grateful for that because it strongly simplifies the delivery procedure overseas. In the future, we will completely change to Bambanker™ in order to improve the survival rate and growth of our cells. We are thankful for resolving that long-standing problem and recommend Bambanker™ to all domestic researchers and foreign cell banks.
This data will be also described at our JCRB website. In the near future we plan to test Bambanker™ for human tissue-derived and human iPS cell lines."
Dr. Arihiro Ohara of the National Institute of Biomedical Laboratories JCRB cell bank.
Stabilization of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
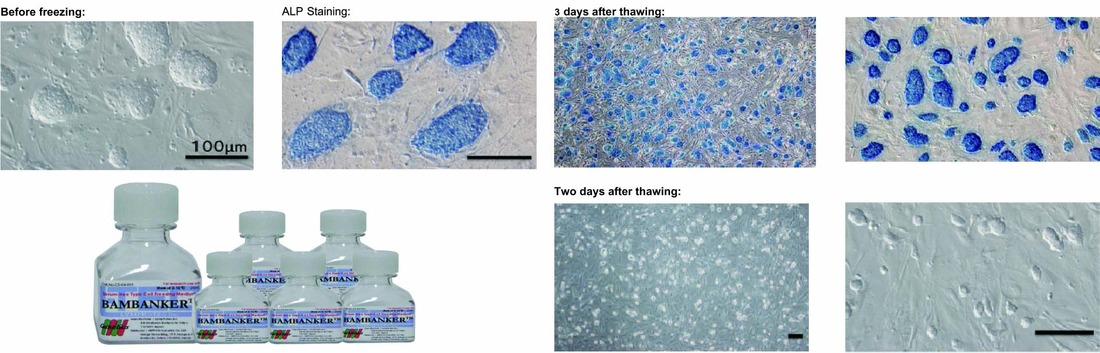
| Cultivation: | 15% FBS/DMEM (1 mM of Sodium pyruvate, 100 µM of NEAA, 100 µM of ß-ME, 1000 U/ml of LIF) was used as culture medium. Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) were used as „feeder cells“. |
| Freezing: | Cells were frozen in 5 vials / ( 60mm dish corresponds to 3.0 x 106 cells/vial ). 1 ml/vial of BambankerTM freezing medium was added and the mixture was directly frozen in -80 °C. The following day, the vials were transferred to liquid nitrogen (slow freezing). |
| Thawing: | Cells were incubated at 37 °C and transferred in cooled culture media. After collection, cells were seeded in 6 well plates and 6 cm dishes. |
| Results: | Stabilization of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells by using BambankerTM was succesful. Cells were undifferentiated, even after freeze and thaw procedure. No modifications of cells could be observed. |
| Datei | Beschreibung | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Application note -JCRB cell bank | Bambanker test and result of JCRB cell bank for 4 very sensitive cell lines | Download |
| Datei | Beschreibung | Link |
|---|---|---|
| MSDS | Material Safety Data Sheet | Download |
| Datei | Beschreibung | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | Protocol for cell freezing | Download |
Hatoya, S. et al. Effect of co-culturing with embryonic fibroblasts on IVM, IVF and IVC of canine oocytes. Theriogenology 66, 1083–1090 (2006).
Hikichi, T. et al. Differentiation potential of parthenogenetic embryonic stem cells is improved by nuclear transfer. Stem Cells 25, 46–53 (2007).
Huang, Y. H., Yang, J. C., Wang, C. W. & Lee, S. Y. Dental Stem Cells and Tooth Banking for Regenerative Medicine. J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2, 111–117 (2010).
Lechner, S. M. Interaktionen von Inseminatbestandteilen mit Epithelzellen und Leukozyten im Uterus des Rindes. (2008).
Liu, D. et al. Relation between human decay-accelerating factor (hDAF) expression in pig cells and inhibition of human serum anti-pig cytotoxicity: Value of highly expressed hDAF for xenotransplantation. Xenotransplantation 14, 67–73 (2007).
Mieno, S. et al. Effects of diabetes mellitus on VEGF-induced proliferation response in bone marrow derived endothelial progenitor cells. J. Card. Surg. 25, 618–625 (2010).
Mieno, S. et al. Characteristics and Function of Cryopreserved Bone Marrow-Derived Endothelial Progenitor Cells. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 85, 1361–1366 (2008).
Naito, H. et al. The advantages of three-dimensional culture in a collagen hydrogel for stem cell differentiation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. - Part A 101, 2838–2845 (2013).
Shimizu, Y. et al. Impaired tax-specific t-cell responses with insufficient control of HTLV-1 in a subgroup of individuals at asymptomatic and smoldering stages. Cancer Sci. 100, 481–489 (2009).
Takata, Y. et al. Generation of iPS Cells Using a BacMam Multigene Expression System. Cell Struct. Funct. 36, 209–222 (2011).
Tamai, Y. et al. Potential contribution of a novel Tax epitope-specific CD4+ T cells to graft-versus-Tax effect in adult T cell leukemia patients after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J. Immunol. 190, 4382–92 (2013).
Zaidi, S. K. et al. Runx2 deficiency and defective subnuclear targeting bypass senescence to promote immortalization and tumorigenic potential. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104, 19861–19866 (2007).
| Cat.No.: | Product | Content |
| BB01 | BambankerTM | 120 ml Freezing medium BambankerTM |
| BB02 | BambankerTM | 5 x 20 ml Freezing medium BambankerTM |
| BB03 | BambankerTM | 20 ml Freezing medium BambankerTM |